 |
The AppCentral
Composite Application Framework is an application development
framework for the Microsoft Windows platform. Using the Microsoft Smart Client
Architecture, the framework allows multiple
applications, known as Applets to be
hosted within the AppCentral runtime environment (known as the
AppCentral Shell), in a similar fashion to Microsoft Outlook
providing E-mail, Contacts, Tasks etc. functions. The
framework provides pre-built components for managing the user
interface, application configuration, navigation, data access,
event management and security etc. in a consistent and uniform
way.
Microsoft defines Smart Client
applications as easily deployed and managed client
applications that provide an adaptive, responsive and rich interactive experience by leveraging local resources
and intelligently connecting to distributed data sources.
See:
http://msdn.microsoft.com/smartclient/understanding/definition/default.aspx
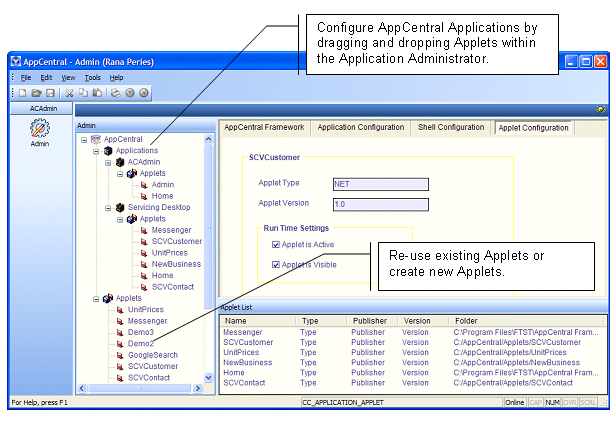
An
AppCentral Application is a collection of one or more AppCentral
Applets hosted within a common runtime environment
known as the AppCentral Shell. The AppCentral Applets are developed using the
Microsoft Visual Studio .NET and the AppCentral class
libraries.
AppCentral
Development Environment
The application
developers use the class libraries provided by AppCentral
(also known as the Client Libraries) to develop AppCentral
Applets, using the Microsoft Visual Studio .NET and the supported languages. One or more
such Applets can be hosted within the AppCentral Shell to form
an AppCentral application.
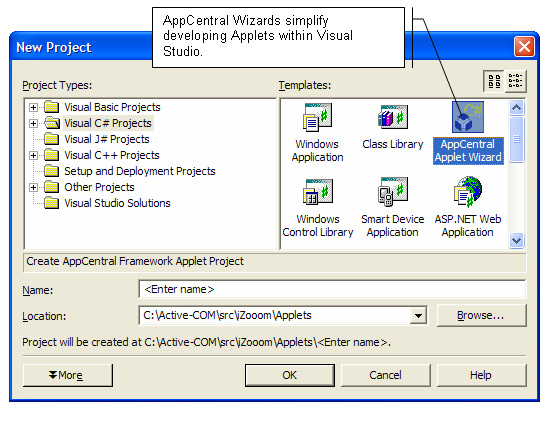
AppCentral Wizards simplify
the Applet development process by guiding the user through the
steps of defining and creating an Applet.
AppCentral
Benefits
-
Migration
Tool - The AppCentral framework supports hosting of
native Windows Applets as well as Microsoft .NET framework
Applets in a common AppCentral Application. This allows
existing investment in Windows C/C++ applications to be
retained whilst new code is developed using the powerful
.NET framework. More importantly, the applications developed
using both types of technologies can be deployed together,
making it seamless for the end user.
-
Enforces
Design Patterns The AppCentral Framework implements the
Model, View Controller (MVC) design pattern. It also ensures
that the components are developed as re-usable components by
providing the framework and the base classes for doing so.
This results in software components that are
re-usable.
-
Service
Oriented Architecture Enablement AppCentral provides a
composite framework within which multiple applications
(Applets) and services can be aggregated, to form one or
more business process. In other words, AppCentral provides a
framework for orchestrating business process that span,
multiple business services.
-
Distributed
Development The development of the individual
Applets can be completely independent of other Applets and
the development can be distributed across multiple
development teams. The Applets developed by individual
developers or teams can be combined in to a single
application through the application configuration
process.
-
Ease
of Deployment AppCentral developed applications can
be deployed in stages, and managed centrally. Once the
AppCentral framework is deployed (for the first
application), deploying the subsequent application can be as
simple as deploying the Applets to a central server. Refer
deployment architecture for further details.
-
Composite
Applications Todays complex business processes
and the underlying requirements often require multiple
applications that perform specific, well-defined functions
to be combined / integrated in to a composite application,
thus providing the user with an integrated environment for
completing the business tasks. AppCentral provides a common
container / environment for hosting multiple (new and
existing) applications.
-
Single
Sign-On The AppCentral Shell controls access to
each of the Applets by ensuring that the user is
authenticated and authorized to access the Applet
functionality. This ensures that a single set of
authentication and authorization credentials can be used to
access multiple Applets.
Platform
Support
The AppCentral
Framework can be used for developing Microsoft .NET framework
applications, native Windows applications or a combination of
the two, making it a very powerful framework for developing new
application or migrating existing
applications to the Microsoft .NET platform.
Architecture
Overview
Utilizing the Model,
View, Controller design paradigm with the Smart Client
application architecture, AppCentral provides a powerful and
flexible Composite Application Framework that
delivers:
-
Responsive
and Rich Interactive Experience through the utilization of
multiple-view architecture that leverages Windows Forms and
the associated user interface controls
-
Intelligent
Connectivity to Distributed Data Sources through
an extensible range of Data Adapters that can be used to
access distributed data
sources.
The
multi-tier architecture of AppCentral is depicted
below:
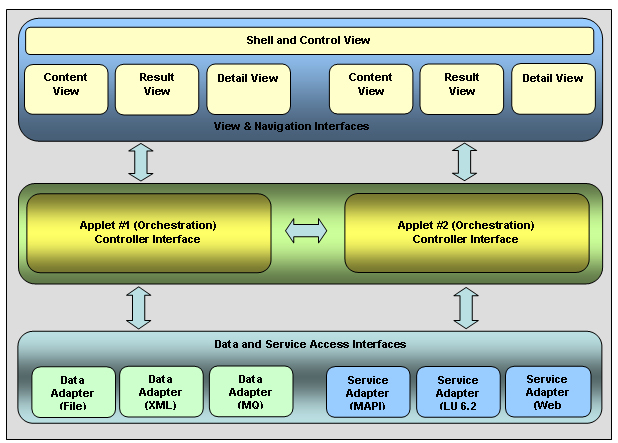
Figure 2-1: AppCentral Composite Application
Architecture
-
Presentation
Tier The presentation tier consists of a
combination of shared and non-shared (applet specific)
components. The Shell and Control view components consist of
the Menus, Toolbars and a Shortcuts bar used for navigation
between the Applets.
Orchestration
Tier The orchestration tier (also known as the
business process tier) represents the Controller components
of the MVC architecture. The Applet objects provide the
controllers. The shared components of this tier provide the
inter-applet integration between multiple
applets.
Data
Tier
The data tier represents the Model or data components of the
MVC architecture. This tier consists of an extensible set of
data adapters that can be used to access a range of
distributed data sources using a consistent
API.
The
presentation tier allows for multiple-views, with each view
capable of displaying the data / information in a specific
layout.
-
Content
View
used for displaying mostly static content for the purpose
of navigation. For example, this view can be used to display
a list or a tree view of contents for navigation
purposes.
-
Result
View
used to typically display results of user operations. For
example, drilling down on contents displayed in the content
view may cause a query to be executed against a remote data
source. The results of this query can be displayed in the
Result View. The Result View is typically represented as a
list or a table.
-
Detail
View
the results displayed in the Result View typically
represents summary information. The detail result objects
are displayed and manipulated within the Detail
View.
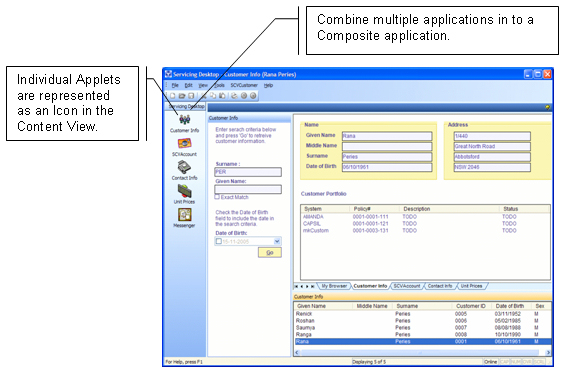
The following
diagram depicts how the various views are organised within the
AppCentral Shell. The AppCentral Shell provides three (3)
panes for hosting the View objects described above. These view
panes are named Content View, Result View and Detail View
respectively. All user interface elements contained within
these views are developed and configured within the Visual
Studio .NET development environment.
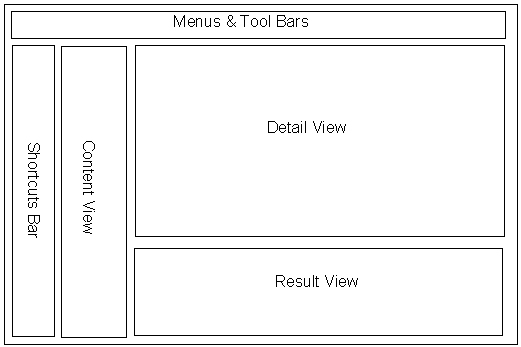
Figure 2-2: AppCentral Shell Architecture
In addition to the Views described above,
the Shell also provides the Menu, Toolbars and a Shortcuts
Bar. The Menus and Toolbars are used to control Applet actions
and are context sensitive. The Shortcuts bar is used for
navigation between Applets hosted within the
Shell.
|
 |